Urine Infection Test (including Cystitis) UTI
From £2.99
This urine infection test is fast & reliable. Result are visible within 2 minutes. This test is suitable for you to do at home and contains all you need to be able to understand your test results. If you obtain an abnormal result with the first strip, repeat the test.
Choose from Two Pack Sizes:
- 2 x Test Strip Pack
- 5 x Test Strip Pack
This urine infection test is fast & reliable with a visible result within 2 minutes. This test is suitable for you to do at home. If you obtain an abnormal result with the first strip, repeat the test using the second strip.
- home health test for Urinary Tract Infections & Cystitis (2 Tests or 5 Tests per pack)
- Fast & Simple Screening Test for urine infection
- Simply dip the test strip in urine for one second
- Wait for 30-60 seconds.
- Compare the colours on the strip to the colour chart.
- No blood required!!
What Is Urinary Tract Infection?
Urinary tract infection is a serious health problem affecting millions of people each year. The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. The kidneys remove excess liquid and wastes from the blood on the form of urine, keeping a stable balance of salts and other substances in the blood. Narrow tubes called ureters carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder, which is a triangle-shaped chamber, in the lower abdomen. Urine is stored in the bladder and emptied through the urethra.
The average adult passes between 0.8 and 2.6 L per day. The amount of urine varies, depending on the fluids a person consumes. The volume formed at night is about half that formed in the daytime. Normal urine is sterile; it contains fluids, salts and waste products, but it is free of bacteria, viruses and fungi. An infection occurs when microorganisms, usually bacteria from the digestive tract, cling to the opening of the urethra and begin to multiply.
In most cases, bacteria first begin growing in the urethra. An infection limited to the urethra is called urethritis. From there, bacteria often move on to the bladder, causing a bladder infection called cystitis. If the infection isn’t treated promptly, bacteria may then go up the ureters to infect the kidneys. This infection is called pyelonephritis.
The urinary system is structured in a way that helps ward off infection. The ureters and bladder normally prevent urine from backing up toward the kidneys, and the flow of urine from the bladder helps wash bacteria out of the body. In men, the prostate gland produces secretions that slow bacterial growth. In both sexes, immune defences also prevent infection. But despite these safeguards, infections still occur.
Escherichia coli (E.coli), a type of bacteria that is normally present in the colon, causes about 80% of urinary tract infections (UTI) in adults. These bacteria may enter the urethral opening from the surrounding skin. Other bacteria that cause urinary tract infections include Staphylococcus, Chlamydia and Mycoplasma.
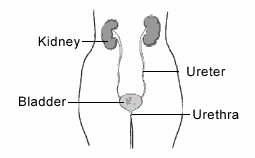
Who Suffers From Urinary Tract Infections?
Urinary tract infections are more common in women than in men. One reason for this is related to the fact that their urethral opening is nearer to the source of bacteria (e.g. anus and vagina) and their urethra is shorter, providing bacteria easier access to the bladder. Another factor is due to the fact that prostate gland in men produces secretions that decrease bacterial growth as mentioned earlier.
What Conditions Increase The Risk Of Urinary Tract Infections?
Certain conditions may increase the risk of developing a urinary tract infection. The most important ones are:
- Bladder outlet obstruction, such as kidney stones or prostate gland enlargement in men.
- Urinary catheterisation (i.e. insertion of a small tube into the bladder through the urethra to drain urine).
- Abnormalities of the urinary tract that is present at birth.
- Suppressed immune system.
- Conditions that cause incomplete bladder emptying such as spinal cord injury.
- In infants, bacteria from soiled nappies can enter the urethra and cause UTI by introducing bacteria in the urinary tract.
Are Pregnant Women More Likely To Get Urinary Tract Infections?
Pregnant women seem to be no more prone to UTIs than other women. However, when a UTI does occur, it’s more likely to travel to the kidneys. Scientists think that hormonal changes and shifts in the position of the urinary tract during pregnancy make it easier for bacteria to travel up the ureters to the kidneys. For this reason, many doctors recommend periodic testing of the urine during pregnancy. Symptoms of urinary tract infection can be divided into two groups; symptoms of lower UTI (Cystitis and Urethritis) and symptoms of upper UTI (pyelonephritis).
What Are The Symptoms Of Lower And Upper UTI In Adults?
Symptoms that indicates lower UTI in adults include the following:
- Back pain
- Blood in the urine
- Cloudy urine
- Inability to urinate despite the urge
- Fever
- Frequent need to urinate
- General discomfort
- Painful urination
How Can You Prevent Urinary Tract Infections?
While urinary tract infections are common, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. Staying well hydrated and urinating frequently can help flush bacteria from your urinary tract before an infection starts. For women, wiping from front to back after using the bathroom also helps prevent bacteria from entering the urethra. Avoiding irritating feminine products and taking showers instead of baths may reduce UTI risk as well. If you do develop a UTI, see your doctor promptly for diagnosis and treatment to prevent the infection from spreading to your kidneys.
Beyond the basics, there are a few more tricks up your sleeve to keep UTIs at bay. Cranberry juice isn’t just an old wives’ tale – it really can help! The fruit contains compounds that make it harder for bacteria to stick to your urinary tract. Not a fan of cranberry? No worries – try adding a probiotic yoghurt to your diet instead. It’ll give your good bacteria a boost, helping to crowd out the troublemakers. Oh, and ladies – cotton undies are your new best friend. They’ll keep things aired out down there, unlike synthetic fabrics that trap moisture and create a breeding ground for bacteria. Remember, a little prevention goes a long way!
Symptoms That Indicate Upper UTI In Adults Include The Following:
- Chills
- High fever
- Nausea (A feeling of sickness in the stomach characterised by an urge to vomit)
- Pain below the ribs
- Vomiting
How Does The Test Work?
The Urinary Tract Infection Check test provides a dip-and-read test strips that are intended for use to check for Leukocytes, RBCs and nitrite in urine specimens as an aid in the diagnosis of UTI. The test provides results by the visual comparison with colour chart printed on the pack.
Procedure:
This procedure MUST BE FOLLOWED EXACTLY to achieve reliable test results.
- Check that the product is within the expiration date shown on he kit pack.
- Prepare the urine specimen.
- Remove the strip from the pouch. Familiarise yourself with the position of the reaction area of Leukocytes, RBCs and Nitrite. Pale pink reaction area is for Leukocytes, white is for nitrite and dark yellow area is for blood. Also, familiarise yourself with the colour chart on the pack

- Dip the test strip in the urine until the reaction areas are completely immersed for no more than 1 second.
- Remove the dipstick from the urine and tap the strip on the rim of the cup to remove excess urine and place it horizontally with the reaction areas facing up.
- Leave the strip for 30-60 seconds for the reaction to take place.
- Read the results by comparing the colours of the reaction on the strip with those of the chart. While comparing, keep the strip in a horizontal position to avoid possible mix of colours between the reaction areas on the strip.
- Identify the best match colour on the colour chart and the correspondent concentration range. A change in colour that appears only along the edges of the reaction areas indicates that the reaction did not take place properly so we recommend redoing the test with another strip.
Results read after 60 seconds are not valid.
Results:
The results are obtained by direct comparison of test strip with the colour chart printed on the pack. See the table below for test interpretation and recommendations.
Related Products
56 reviews for Urine Infection Test (including Cystitis) UTI
| 5 star | 94 | 94% |
| 4 star | 5 | 5% |
| 3 star | 0% | |
| 2 star | 0% | |
| 1 star | 0% |




Anonymous (verified owner) –
Easy to order and quick service
Patricia Hemsley (verified owner) –
Suzanne Hooper (verified owner) –
Easy to order and fast delivery. Good company
Amanda (verified owner) –
Fast delivery and product as described thank you !!!
Tony (verified owner) –
Very fast service
Dawn (verified owner) –
Accurate test,easy to use arrived very promptly
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Excellent
Caroline (verified owner) –
Straightforward ordering and the package was processed and delivered promptly. Instructions for the test were comprehensive and the subsequent results enabled me to secure appropriate medication from my GP surgery.
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Arrived qluick product l100%
Shirley (verified owner) –
I received order very quickly
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Simple to use and understand
D M. (verified owner) –
Delivered promptly and extremely easy to use.
Yoliswa Poswa (verified owner) –
Kathleen (verified owner) –
Very efficient and quick delivery
Keith (verified owner) –
Excellent service and product to your usual good standards.
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Great product and ultra accurate!
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Good product.
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Not used yet but delivery time was amazing
Helen (verified owner) –
Very fast delivery easy to use
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Came quickly, did the job, good price, no problems
Michael (verified owner) –
Miss j. (verified owner) –
Test strips arrived super fast, well packed. Could of done with a tad more information on the list, as my ph was high, nitrates on first test (but not on the repeat the following day? & SG read fairly high but not sure what that realy means… The others were either neg, or trace… Good to know I’m not so unwell as feared…
Sharon Sykes (verified owner) –
So pleased I could get this online very happy with service
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Ordered Friday arrived Mon. Very pleased
Marina (verified owner) –
quick and reliable. thanks
Maria Caires (verified owner) –
elaine (verified owner) –
prompt delivery very reasonable price
MR (verified owner) –
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Daniela cozaciuc (verified owner) –
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Peter S. (verified owner) –
Good value, promptly received.
juliet w. (verified owner) –
Arrived promptly. Well packaged. I don’t yet need to use them but it is reassuring to have them at hand . Also reasonably priced and good to be able to buy small quantities of test strips instead of a large bottle which once opened has a very limited life as the strips oxidise quickly
Christine J. (verified owner) –
Easy to use
Rosemary P. (verified owner) –
Haven’t used them yet, got them as a standby…very good service though.
keith (verified owner) –
brilliant product realistically priced , speedy delivery as always.
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Good thanks
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Bridget (verified owner) –
Easy to order and fast delivery great price
Keith (verified owner) –
Excellent swift service, highly recommend this company.
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Anonymous (verified owner) –
keith (verified owner) –
Excellent service and great attitude from John
Kirsti (verified owner) –
These are very affordable and came very quickly in the mail considering the current situation. Like others here, I got this since I’m having some UTI symptoms and yet don’t want to bother the NHS about if it’s not serious. The test was clearly explained and informative. I got a negative result, which I can only assume is correct. It would have been good to know, however, that the tests all have to be used immediately as they are all in the one foil packet. I bought a 5 pack thinking I could retest later, but apparently now the packet is open, they are not necessarily valid.
Anthony Cunningham (store manager) –
Many thanks for taking the time to post a review – it is much appreciated and will help others who are considering this product.
As to your question regarding the foil containing the test strips, once the pouch has been opened, the remaining strips remain stable for up to 30 days as long as the pouch is immediately re-sealed. We will try and make this a bit clearer in our instructions.
Thanks again for the feedback!
Martin Knight (verified owner) –
Excellent service thank you
Wendy (verified owner) –
Great service thank you and especially at this it saved me going to GP unnecessarily
Alison (verified owner) –
Very swift delivery, thank you!
Clare (verified owner) –
This was easy to use and because it provided a positive result I felt justified in phoning my GP for antibiotics. A brilliant tool to use in the current pandemic when I’m avoiding going out as much as possible.
Anonymous (verified owner) –
Excellent speedy service, thank you
Mrs Sheila D. (verified owner) –
A very speedy service. Thank you.
Krystyna Gorka (verified owner) –
Very good seller
sarah (verified owner) –
Far delivery thank you under the circumstances
Sally –
My doctor actually recommended this test to me as it is exactly the same as the one she uses in her surgery. I have suffered from recurring UTI’s over the last few years. Having a supply of these tests on hand allows me to check my urine for possible UTI’s. I now get results in minutes, rather than having to ring the doctor and wait days for an appointment. Great for peace of mind.
Skater Girl (store manager) –
I bought this test because I was worried that I had a urine tract infection. The test was simple to use and I got a positive test when I used it so I went to see my GP who confirmed the result and prescribed medication. The test gave me the confidence to talk to my doctor about my problem. As well as being a very easy to use test, it was also very cheap (much cheaper than similar I seen at the chemist shop) and it arrived next day after ordering. Thank you Zoom Health!